Thanks to the advance of computer and network technologies, we can now easily share and utilize data of large volume and high diversity which we cannot even think about until decades ago. It has been changing our society and daily life. This environment relies on technologies for collecting, analyzing, and extracting various kinds of information, and for retrieving relevant information from it. Our research purpose is to enhance these technologies, and to make all useful information in the world easy to share and utilize.
1. Social information analysis based on Web data
Today’s Web is an important resource of information on the “offline” world. The Web can be a good sensor of the society. Data on the Web are, however, biased in various ways, and we need to remove such biases to obtain the accurate information on the society. Our goal is to develop methods of removing such biases.
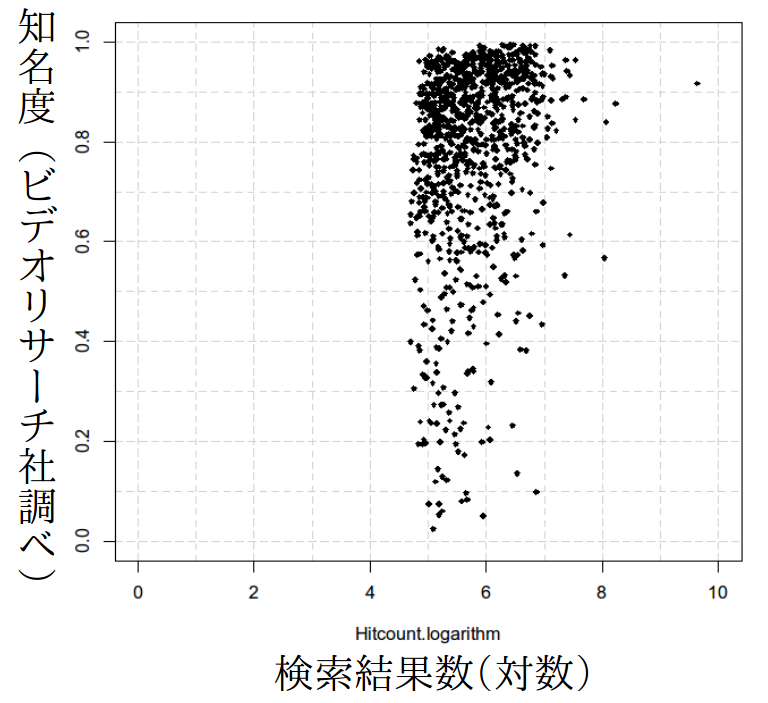 |
 |
|
| Y: fame (the ratio of people who recognize the person) for 1,000 celebrities and X: Web search hit count of their names (log scale). Data on the Web are biased and we cannot approximate the fame in the real world simply by the Web search hit count. | To know the real-world accurately through the Web data, we need methods to remove biases from the Web data. |
2.Social Network Analysis
Online social network is one of useful resources of information on the real world. It is especially useful for individual-level information and real-time information. We are developing methods of extracting useful information from this valuable data resource.
Examples of research in this topic:
| Classification of Twitter follow relationship [Tanaka, Takemura, Tajima, ACM HT2014] |
Discovery of early adopters on Twitter [Imamori, Tajima, ACM CIKM2016] |
|
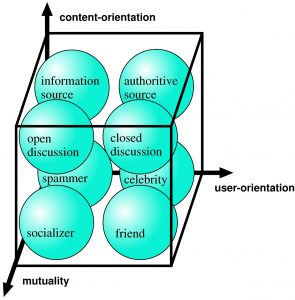 |
 |
|
| Three axes for classifying user relationship on Twitter (content-orientation, user-orientation, mutuality). For example, a follow edge to a celebrity is usually not topic-oriented (interest is not limited to a specific topic), but is user-oriented (interest is specific to that person, and the follower is not necessarily interested in other person even if the person’s posts are in the same topic), and not for mutual communication (mainly for one-way communication). | On Twitter, there are users called “early adopters (EAs)” who are the first to discover and follow new and useful information sources. If we can discover such early adopters, we can use them for various applications. For example, it can be used to predict the future popularity of a new Twitter user. Even if a new user currently has a small number of followers, if the current followers include some early adopters, such a new user is likely to become popular in the future. Such an early adopter has many followers himself, and when an early adopter follows a certain information source S, many followers imitate and follow S, too. Therefore, many triangles like those shown in the figure above are formed. Therefore, we developed a method to discover early adopters by counting these triangles. |
3.Crowdsourcing
It is often said that artificial intelligence will take jobs away from humans, but the ideal would be to achieve an optimal division of roles between humans and artificial intelligence. As part of our research to achieve such a world, we are conducting research to realize the optimal role-sharing in cooperative work between humans and artificial intelligence, especially in combination of “crowdsourcing” and “machine learning.”
| The logo of CyborgCrowd Project |
 |
| Red circles represent human, black circles represent AIs, and the entire logo represents the cooperation of human and AI. |
Example of research in this topic:
| Best Task Assignment in Multi-class Classification Tasks through Hierarchical Classification Schemes [Duan, Tajima, WWW Conf. 2019] |
 |
| We consider a task of classifying photos of seven different canis species and dog breeds. If the workers include both dog enthusiasts who are knowledgeable about dog breeds and experts specializing in wild animals, it would be more effective to transform the classification task into a hierarchical structure with three subtasks, as shown in the figure above, rather than having everyone classify all images into seven categories. Specifically, we first ask a worker to classify images into two classes: “dogs” and “wild animals.” Then, images classified as dogs would be assigned to workers who are knowledgeable about dog breeds, and are further categorized into the dog breeds, while those classified as wild animals would be handled by experts in wild animals. This hierarchical approach is expected to improve classification accuracy. Additionally, if artificial intelligence can reliably perform the initial broad classification between dogs and wild animals, AI can take on that part of the task. However, when given a multi-class classification task, determining the optimal classification hierarchy is not trivial. Therefore, we have developed a technique to discover the best classification hierarchy. |
4.Information Access Interface
In the past, the most important factor in processing large amounts of information was improving the speed of computation. However, today, computers are often fast enough, and the bottleneck is often the human ability to review the huge amount of output. Therefore, we are conducting research on user interfaces that enable humans to efficiently browse large volumes of information.
Example of research in this topic:
| a Web browser representing open tabs by thumbnails [Liu, Tajima, ACM IUI2010] |
 |
| When opening multiple web pages in a browser using tabs, it sometimes become difficult to identify which tab corresponds to which page. To address this, we developed a browser that displays thumbnails of web pages instead. However, when displaying a large number of thumbnails, each thumbnail becomes smaller, making it hard to distinguish between similar pages from the same website. To solve this issue, our browser enlarges and highlights two key elements within the thumbnail: the site’s logo and the most important image on the page. Displaying these two elements allows users to differentiate most web pages effectively. |
5.Information Retrieval
When it comes to web search, the established style is to enter keywords and receive a list of snippets of related web pages. However, this current format is not necessarily always sufficient or optimal. Every day, a vast number of people spend an enormous amount of time on information retrieval, making the improvement of this process an important societal challenge.